Kubernetes的学习
Intro to K8s
What is Kubernetes?
Official Definition
Kubernetes, also known as K8s, is an open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
Open source container orchestration tool
Developed by Google
Helps you manage containerized applications in different deployment environments
(physicl / virtual / cloud )
Problem-Solution case study
What are the tasks of an orchestration tool?
The need for a container orchestraton tool
The rise of containers and the microservice technology actually resulted in applications that they’re now comprised of hundreds or sometimes maybe even thousands of containers now managing those loads of containers across multiple environments using scripts and self-made tools can be really complex and sometimes even impossible
- Trend from Monolith to Microcervices
- Increased usage of container
- Demand for a proper way of managing those hundreds of containers
What features do orchestration tools offer?
High Availability or no downtime
high availability means that the application has no downtime so it’s always accessible by the users
Scalability or high performance
application has high performance it loads fast and the users have a very high response rates from the application
Disaster recovery -Backup amd restore
the infrastructure has to have some kind of mechanism to back up the data and to restore it to the latest state so that application doesn’t actually lose any data and the containerized application can run from the latest state after the recovery
Main K8s Components
Node and Pod
Node
a worker machine(工作机)
a simple server a physical virtual machine depends on the cluster
Node也被称为Worker或Minion,是部署容器(工作负载)的单机器(或虚拟机)
Pod
Smallest unit of K8s
Abstraction over container 容器上的抽象
Containers should only be scheduled together in a single Pod if they are tightly coupled and need to share resources such as disk.
Usually 1 applicaion per Pod
Each Pod gets its onw IP address
New IP address on re-creation
Service and Ingress
Service
- permanent IP address
- lifecycle of Pod and Service NOT connected
External service
http://my-app-service-ip:port —> http://124.89.101.2:8080(test) —> https://my-app.cpm
Internal serivece
Ingress
—External service
request goes first to ingress and it does the forwarding then to the service
Configmap and Secret
Use them as environment variables or as a properties file
tradition:
re-build —> push it to the repo —> pull it fro the repo
Configmap
- external configuration of your application
- Don’t put credential into Configamp
Secret
- used to store secret data
- based64 encoded
- (The built-in security mechanism is not enabled by default)
Volumes
data storage
container pr pod restarted, the data will be gone
Volumes attached a physical storage on a hard drive to the pod
- Storage on local machine
- or remote, outside of the K8s cluster
distinction betweeen the kubernetes cluster and all of its components and the storage
think of the storage as an external drive plugged in into the kubernetes cluster
K8s doesn’t manage data persistance
Deployment and Stateful Set
The replica is connected to the same Service
Service has 2 functionalities:
- permanent IP
- load balancer
Deployment
- blueprint for my-app pods
- you create Deployments (can specify how many replicas and can also sacle up or down the number of pods needed)
- abstraction on pods
in practice, mostly words with the deployment and not with pods
We need replicate database as well, but DB can’t be replicated via Deployment because database has a state. All need
to access to the shared data storage.
need a machanism to avoid inconsistencies (pods writing or reading)
StatefulSet
the feature in addition to replicationg feature is offered by StatefulSet
for STATEFUL applications
like elastic, mongoDB, MySQL
Depolyment for stateLess Apps
StatefulSet for stateFul Apps or Databases
but deploying StatefulSet in k8s is not easy. So DB are ofthen hosted outside of K8s cluster.
Main Kubernetes Components summarized
abstraction of containers — Pod
communication — Service(in communication between pods)
roue traffic into cluster — Ingress(used to route traffic into the cluster)
external configuration — configmap/secret
data processing — volumes
pod blueprints with replicating mechanisms — Deployment / StatefulSet
(StatefulSet is used specifically for stateful applications like databases)
Kubernetes Architecture explained
Node processes
Two types of nodes
- master
- slave
Worker machines in K8s cluster
each Node has multile Pods on it
3 processes must be installed on every node
Container runtime
比如docker, 或者别的虚拟化技术
Kubelet
Kubelet interacts with both - the container and node
Kubelet starts the pod with a container inside
process schedules those pods then underneath
a process of kubernetes itself
responsible for taking configuration and actually running a pod or starting a pod with a container and then assigning resources from that node to the container (like cpu ram and storage resources)
usually kubernetes cluster is made up of ,ultipe nodes which also must have container runtime and kubelets installed. you can have hundreds of those worker nodes which will run other parts and containers and replicas of the existing parts like my app and database
communcation betweeen them uses Services, whihc is a sort of balance that basiclly cathes the request directed to the pod or the applcaition like database and then forwards it to the respective pod and the third process that is responsible for forwardiung requests form services to pods is actually Kube proxy
Kube proxy
Kube Proxy forwards the requests
must be installed on every node
intelligent forwarding logic inside that makes sure the communication works in a performative way with low overhead
Worker Nodes do the actual work
How to interact with this cluster?
How to:
- sechedule pod?
- monitor?
- re-schedule /re-start pod?
- join a new Node?
Managing processes are done bu Master Nodes
Master processes
4 processes run on every master node that control cluster state and the worker nodes
Api server
cluster gateway
get the initial request of updates into the cluster or even the query from the cluster
use some ui, like kubernetes dashboard, command line or api
acts as a gatekeeper for authentication
流程:
some requests —> API Server —> validates request —> other processes —> Pod
good for security because only 1 entrypoint into the cluster
Scheduler
流程:
Schedule Pod —> API Server —> Scheduler —> where to put the Pod —> Kubulet
Scheduler just decides on which Node new Pod should be scheduled
(Kubulet starts a podwith a container)
Controller manager
detect cluster state changes (like crashing of pods)
流程:
Controller Manager —> Scheduler —> Kubelet —> Pods
etcd
a key value store of a cluster state
- etcd is the the cluster brain
- Cluster changes stored in the key value store
cluster state data
- Is the cluster healthy?
- what resources are available?
- Did the cluster state change
Application data is NOT stored in etcd
kubernetes cluster is made up of multiple masters where each master node runs its master processes, where the
- api server is load lalanced
- etcd store forms a Distributed storage across all master nodes
Example Cluster Set-Up
In a very small cluster, you probably have 2 Master Nodes and 3 +++Worker Nodes
and hardware reousrces of master and node servers differ
master — more important / less resources
worker nodes — more resources
Add new Master / Node server
- get new bare server
- install all the master / worker node process
- add it to the cluster
Minikube and Kubectl - Local Setup
What is minikube
Production Cluster Setup
- Multiple master and Worker nodes
- Separate virtual or physical machines
Test on local machine?
Test/Local Cluster Set up
minikube is basically one node cluster where the Master and Node processes run on ONE machine
This node will have docker runtime pre-installed, so could ru the containers or the pods with container on this node on your laptop through a vrtual box or some othe rhypervisor
minikube
- creates Virtual Box on you rlaptop
- Node runs in that Virtual Box
- 1 Node K8s cluster
- for testing purposes
What is Kubectl
need some way to interact with a cluster, want to create components configure etcd
a command line tool for kubernetes clusters
Master process — Api Server enable interaction with cluster (the main entrypoint into the kubernetes cluster)
if want to do anything to kubernetes, configure anything, create any components, you first talk to api server. You have to use different clients , so you have a ui like a dashboard you can talk to it using kubernetes api, or a command line tool which is kubectl
Kubectl is the most powerful of 3 clients
enable pods to run on node (create pods, destory pods, create services)
kubectl isn’t just for minikube cluster
kubectl is a tool used to interacts with any type of kubernetes cluster setup
Installation and create minikube cluster
(virtualization on the machine needed)
Step 1: Install Hypervisor
Step2:Install Minikube
安装Minikube的时候,kubectl也会安装好
minikube start
有了docker就不用hyperkit
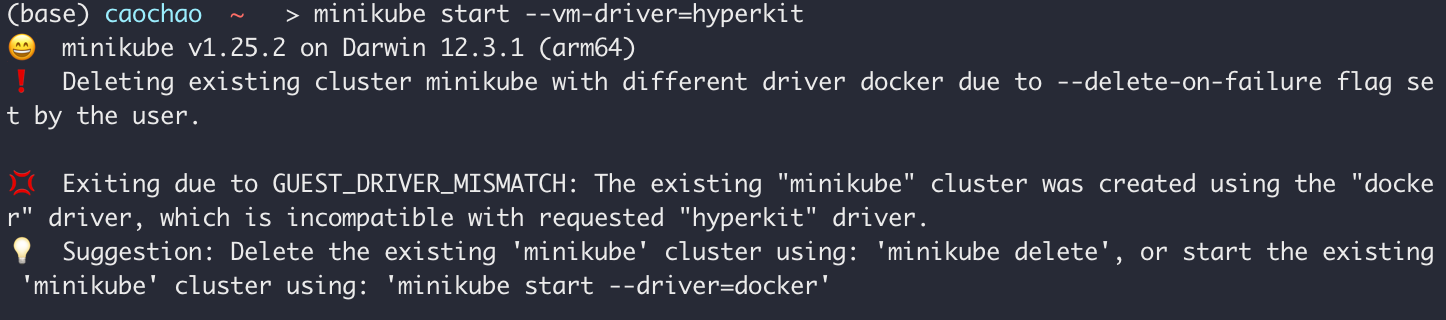
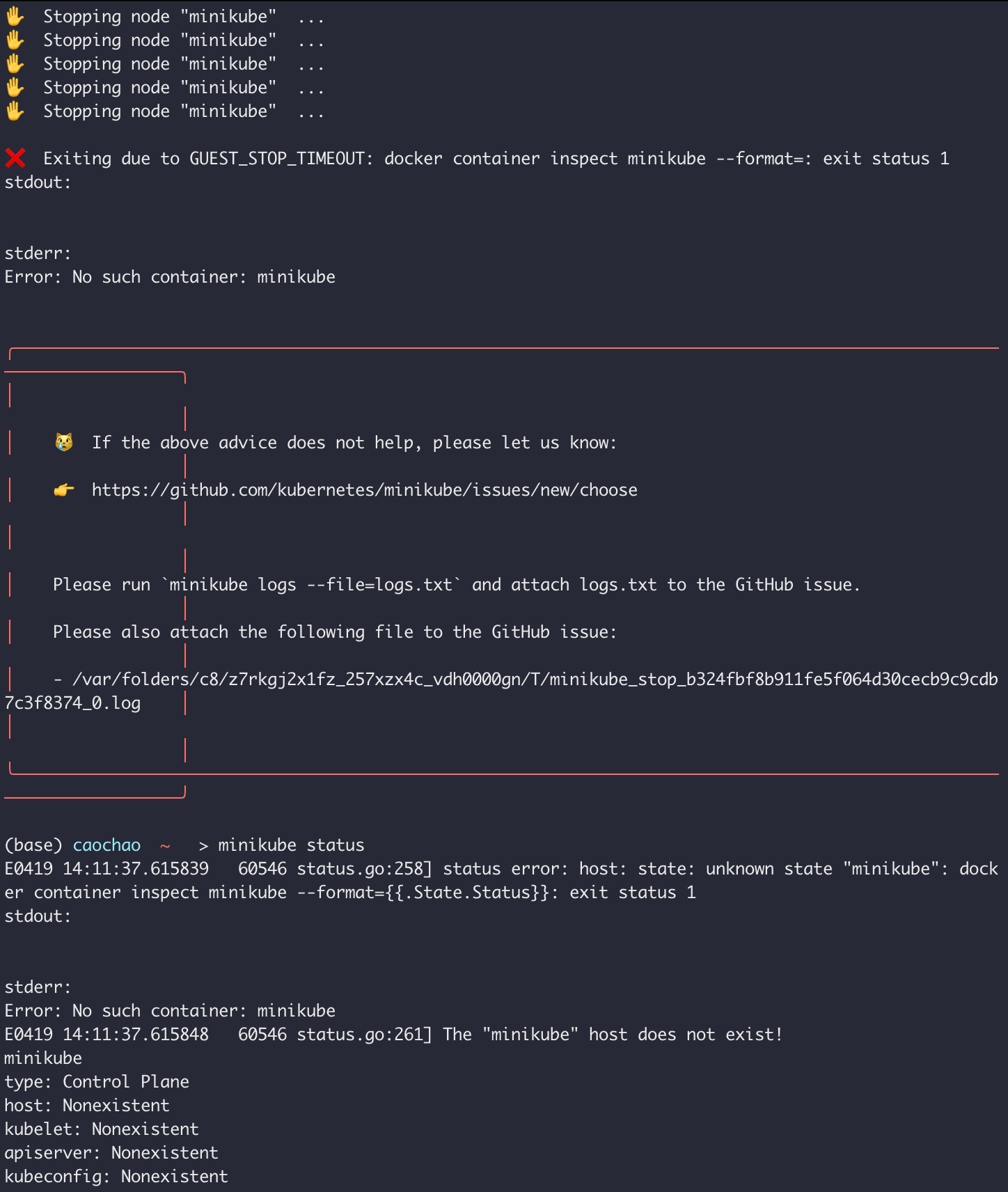
minikube start
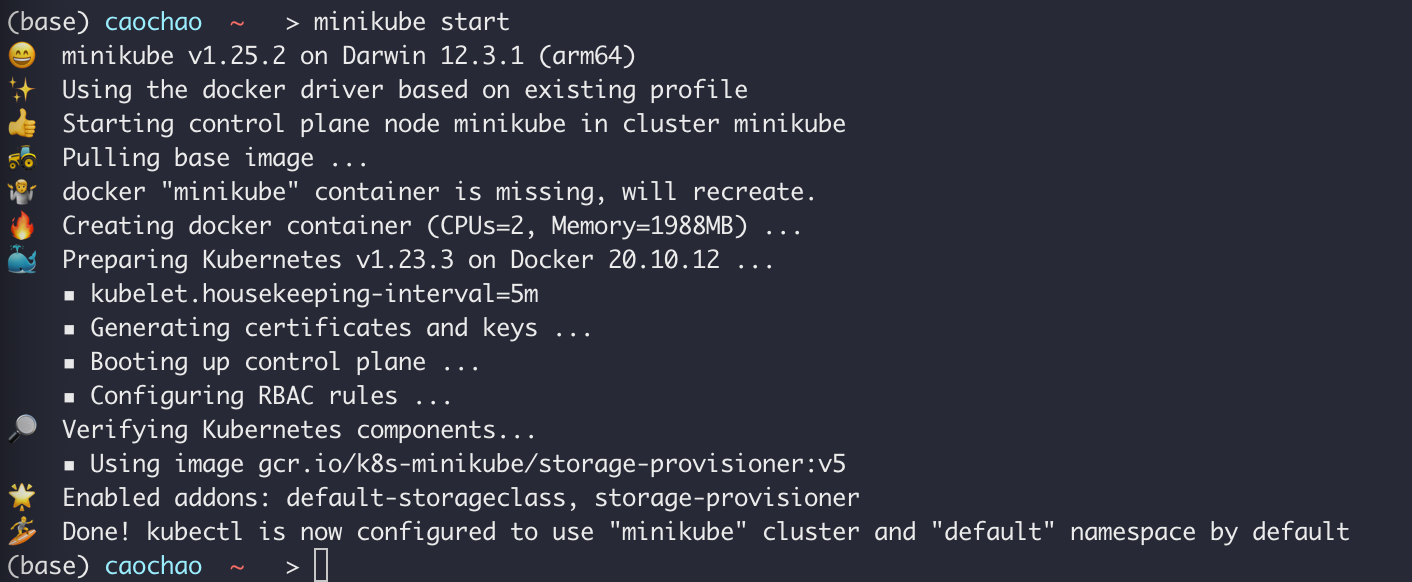
Kubectl get nodes
get status of nodes
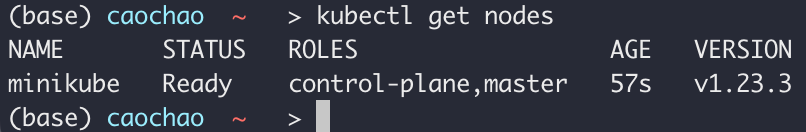
Minikube status

kubectl version
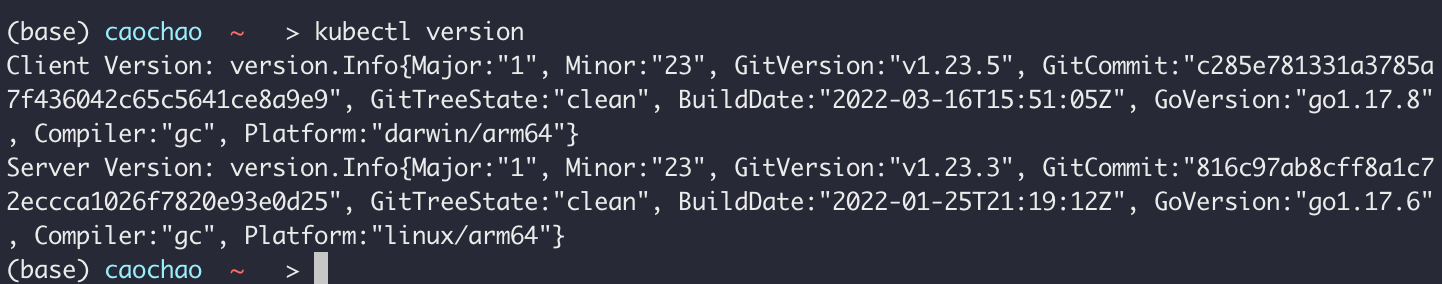
(Client version + Server Version indicate that minikube is correctlly installed)
Kubectl CLI
for configuring the Minikube cluster
Minikube CLI
for start up/deleting the cluster
Main Kubectl Commands - K8s CLI
Pre-requisities:
- minikube installed
- kubectl installed
Basic kubectl commands
Get status of different components / Create and Edit a Pod
- kubectl get nodes
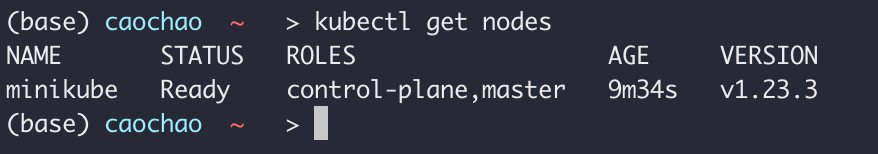
- kubectl get pods
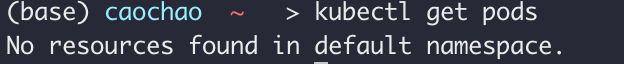
- Kubectl get services
kubectl create -h
Pod is the smallest unit. But you are not creating pods …
Deployment - abstraction over Pods
Usage:
kubectl create deployment NAME –image=image [–dry-run] [options]
- Blueprint for creating pods
- most basic configuration for deployment (name and image to use)
- rest defaults
kubectl create deployment nginx-depl –image=nginx

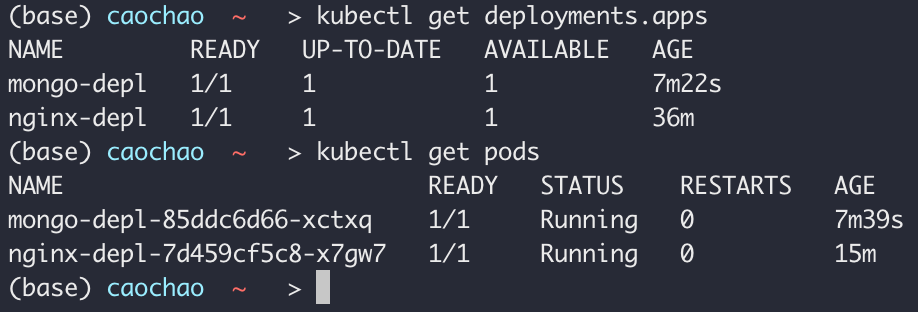
kubectl get deployment
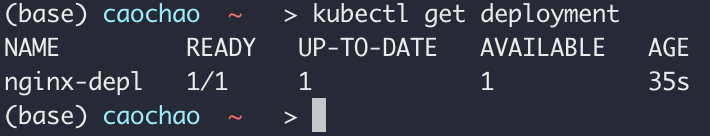
kubectl get pod
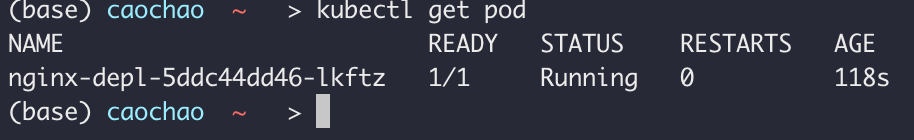
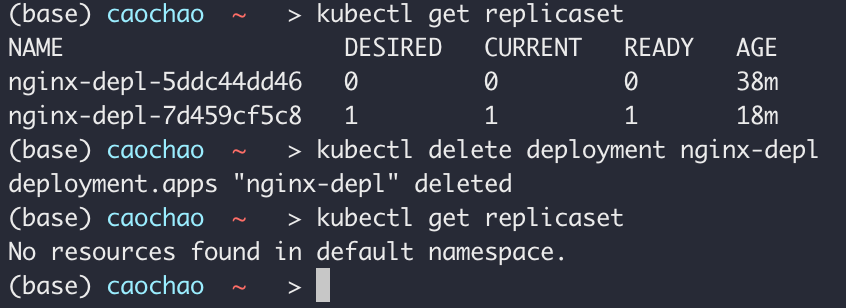
kubectl get replicaset
Replicates is managing the replicas of a Pod
Layers of Abstraction
- Depolyment manages a rs
- ReplicaSet manages a pod
- Pod is an absratction of Container
- Container
Everything below Deployment is handled by Kubernetes
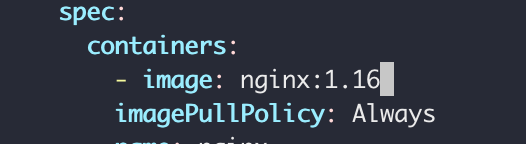
kubectl edit deployment [name]
and we get auto-generated configuration file with default values
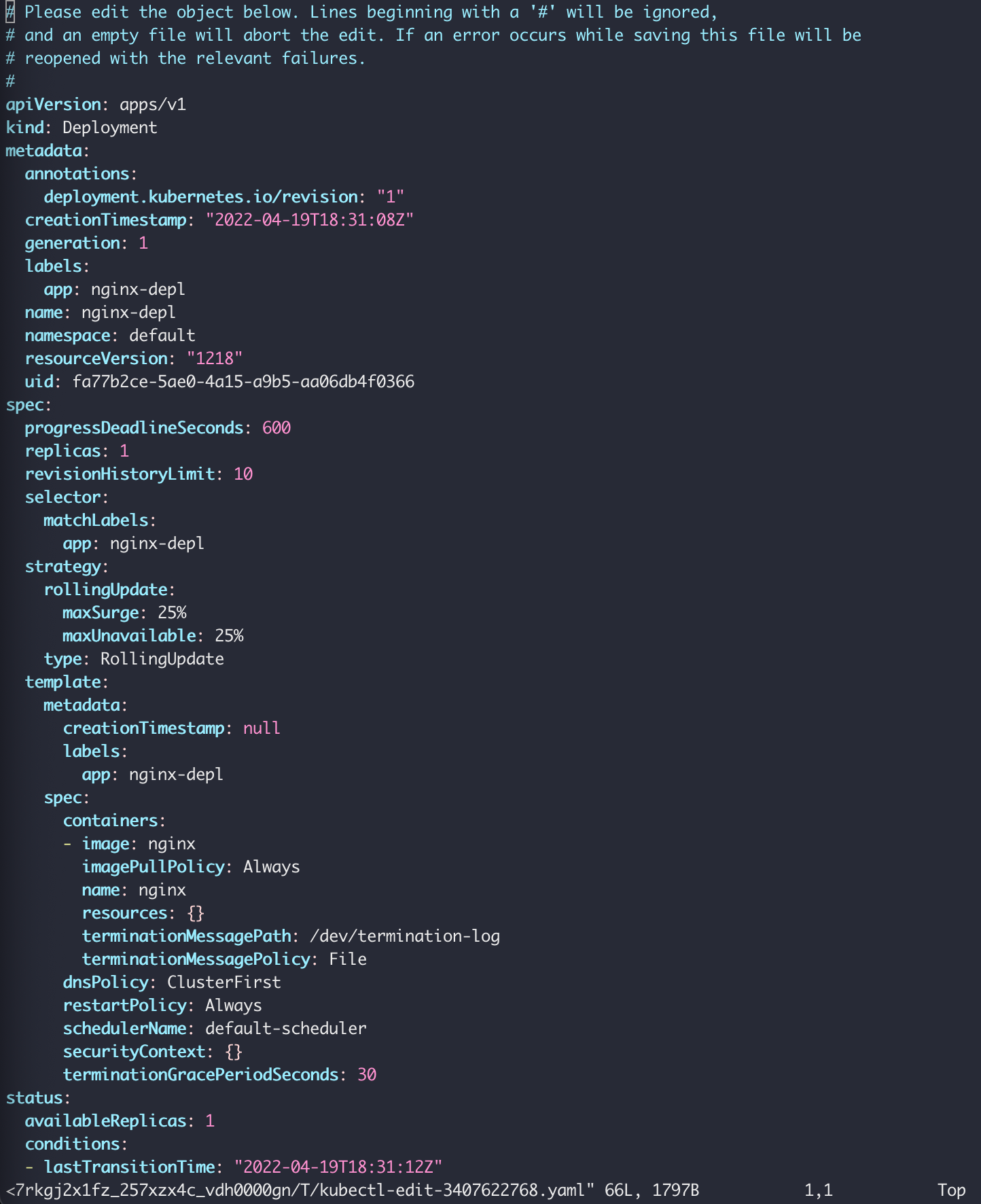
修改image版本
Save the change 
kubectl get pod检查
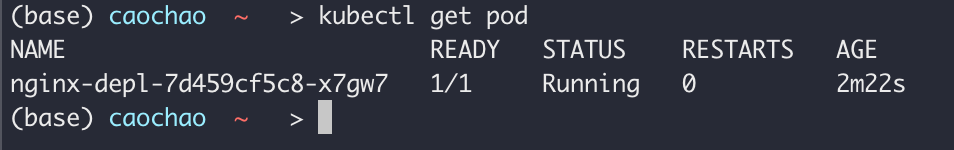
We can get a new one with a new image
Kubectl get replicassets
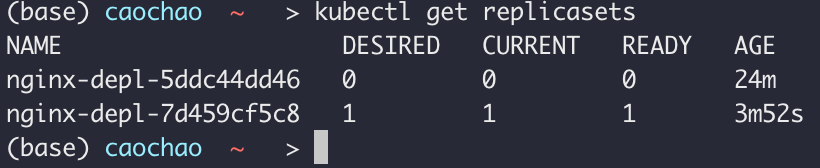
Debugging pods
kubectl logs [pod name]
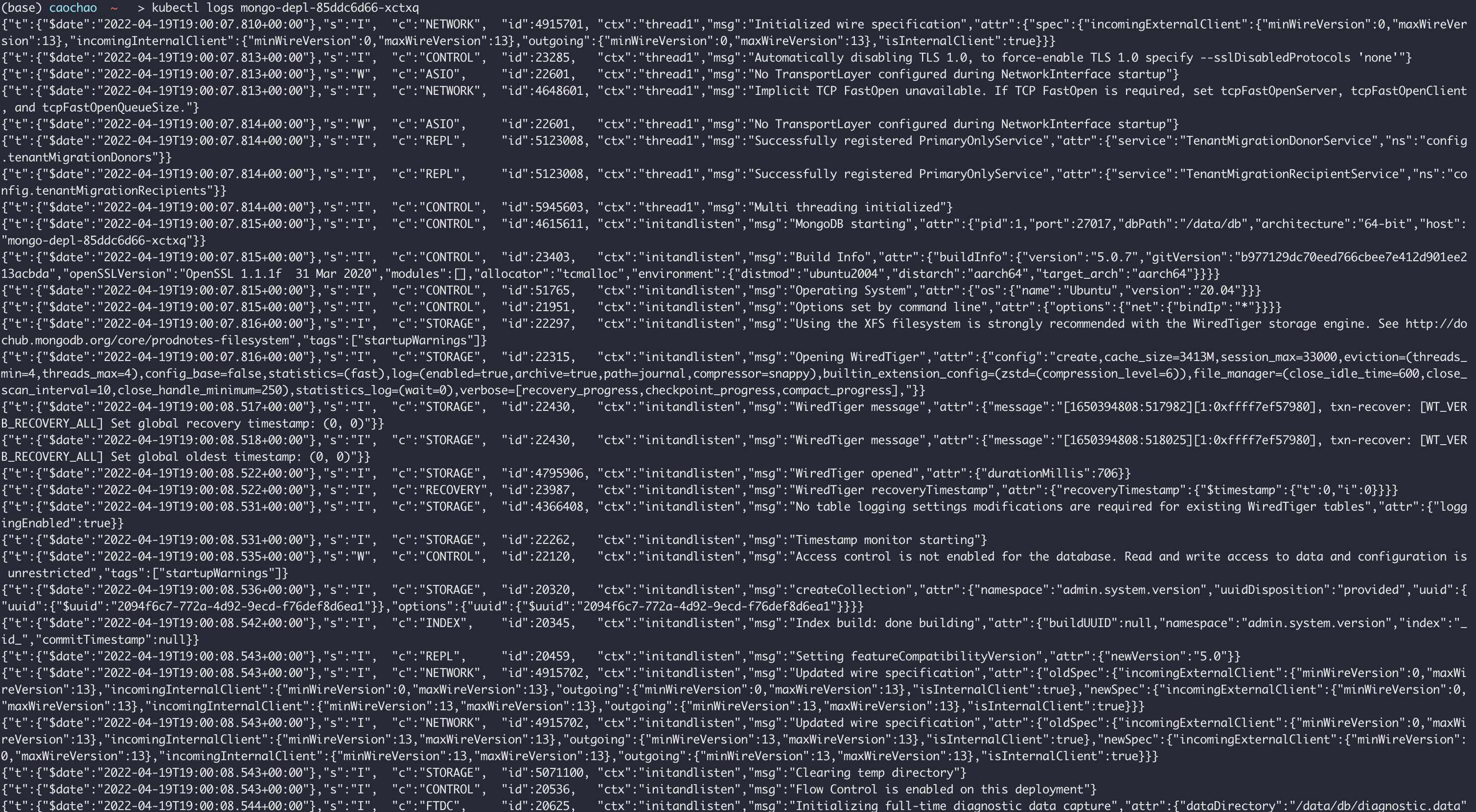
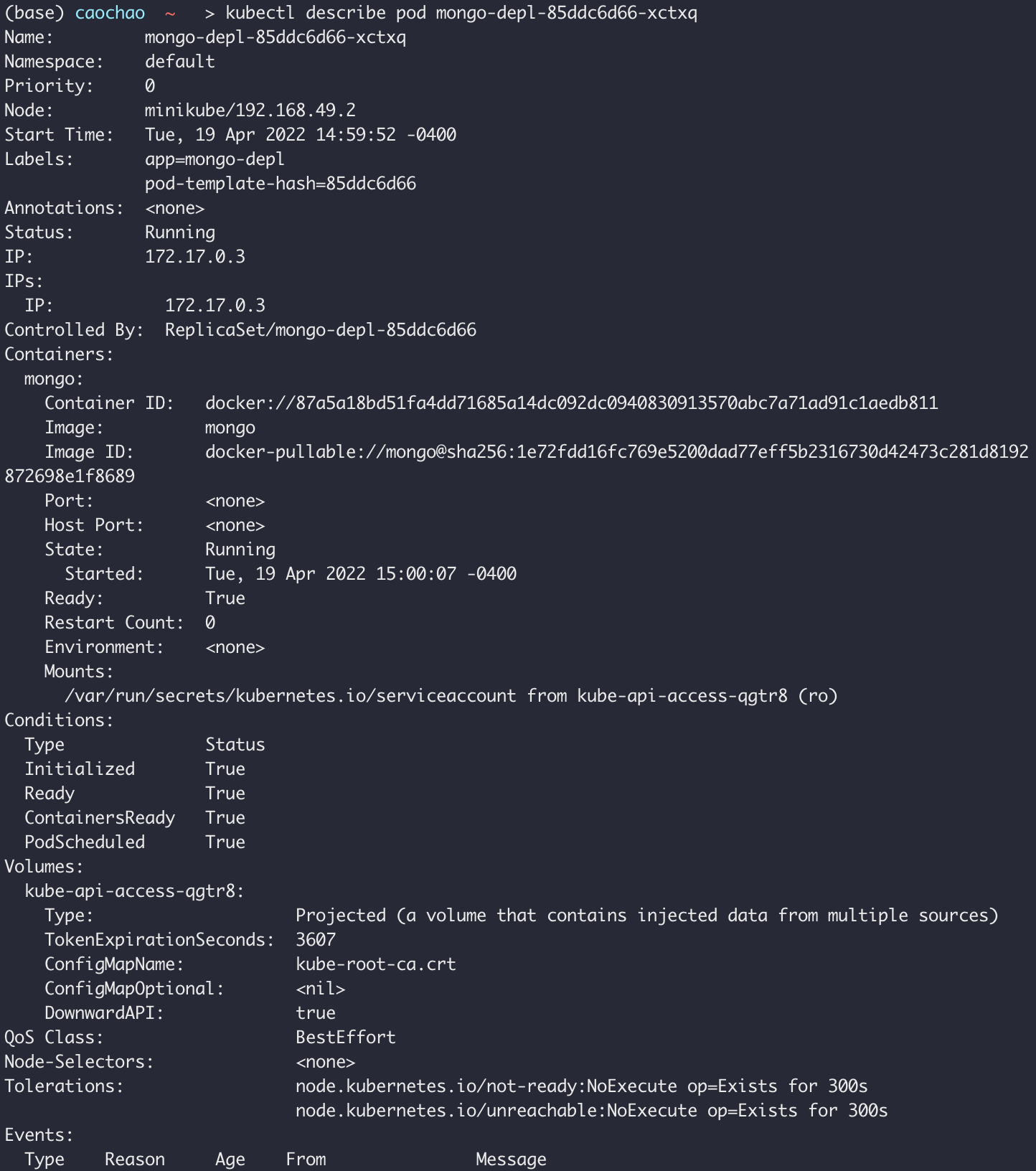
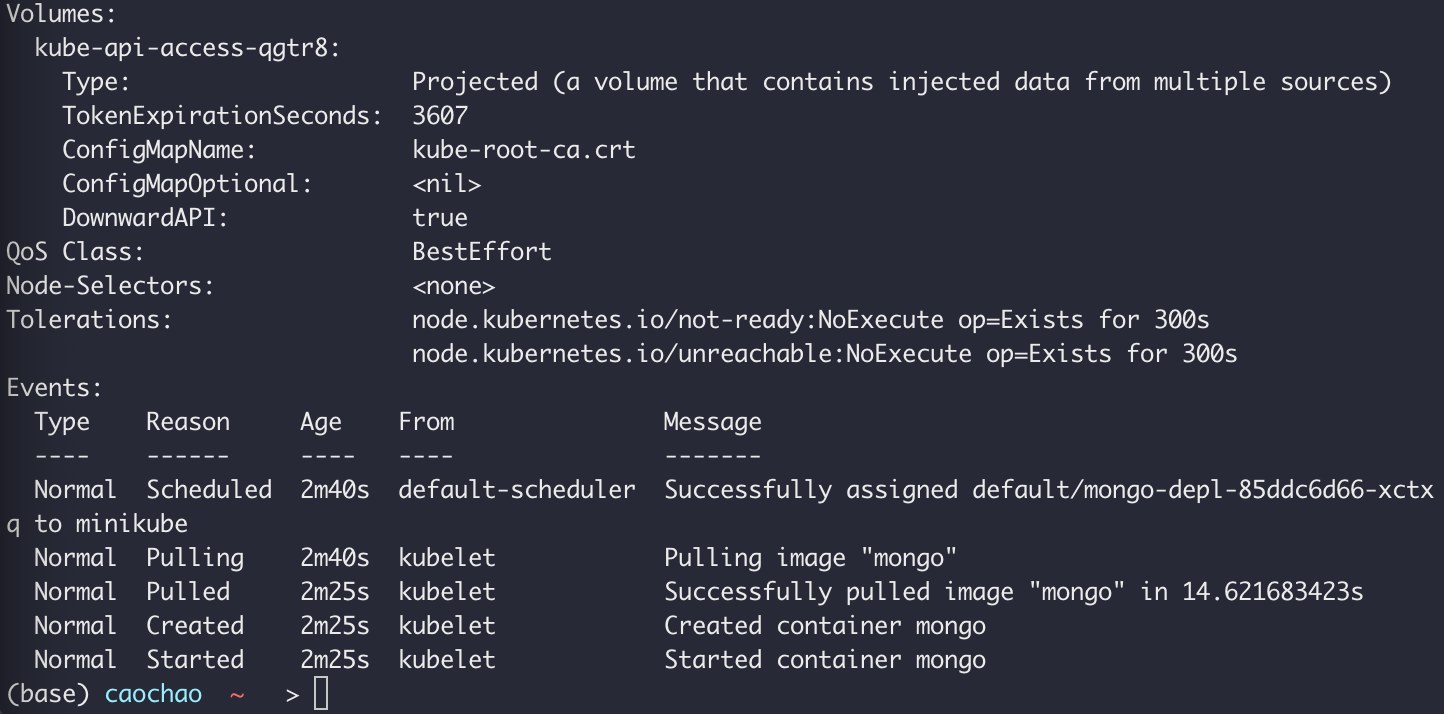
Kubectl describe pod [pod name]
kubectl exec-it [pod name] – bin/bash
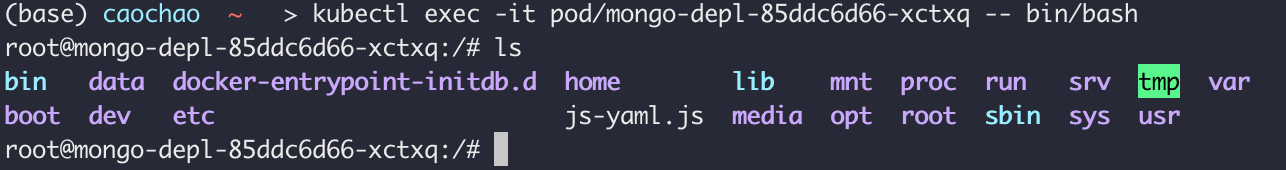
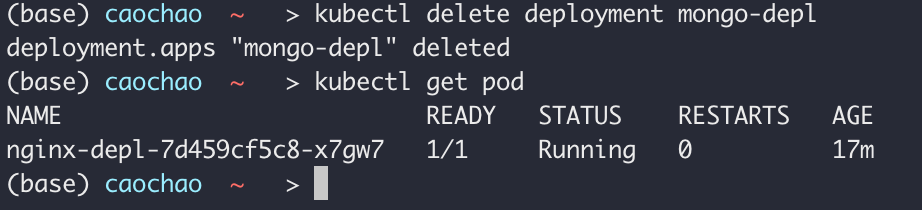
kubectl delete deployment mongo-depl
kubectl get replicaset
kubectl create deployment name omage option1 option2
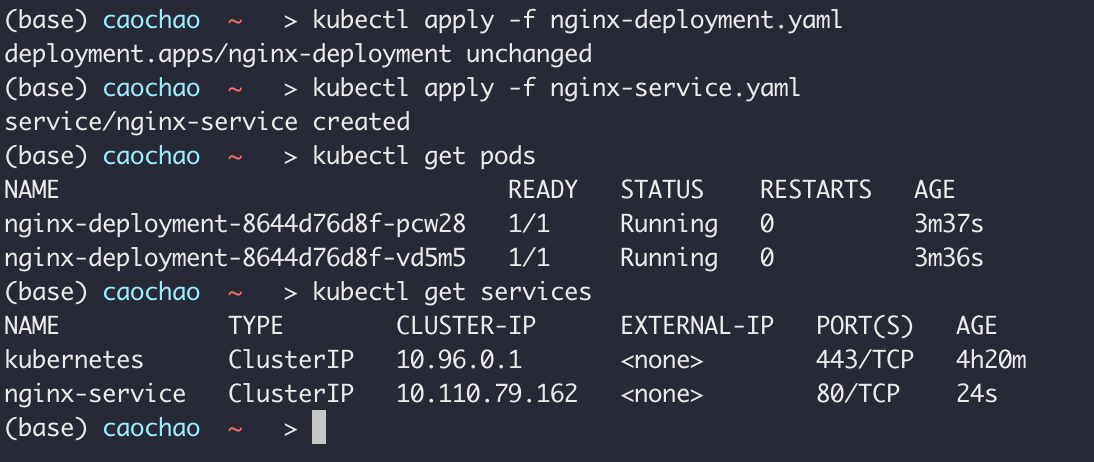
kubectl apply -f [file name]
kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yaml
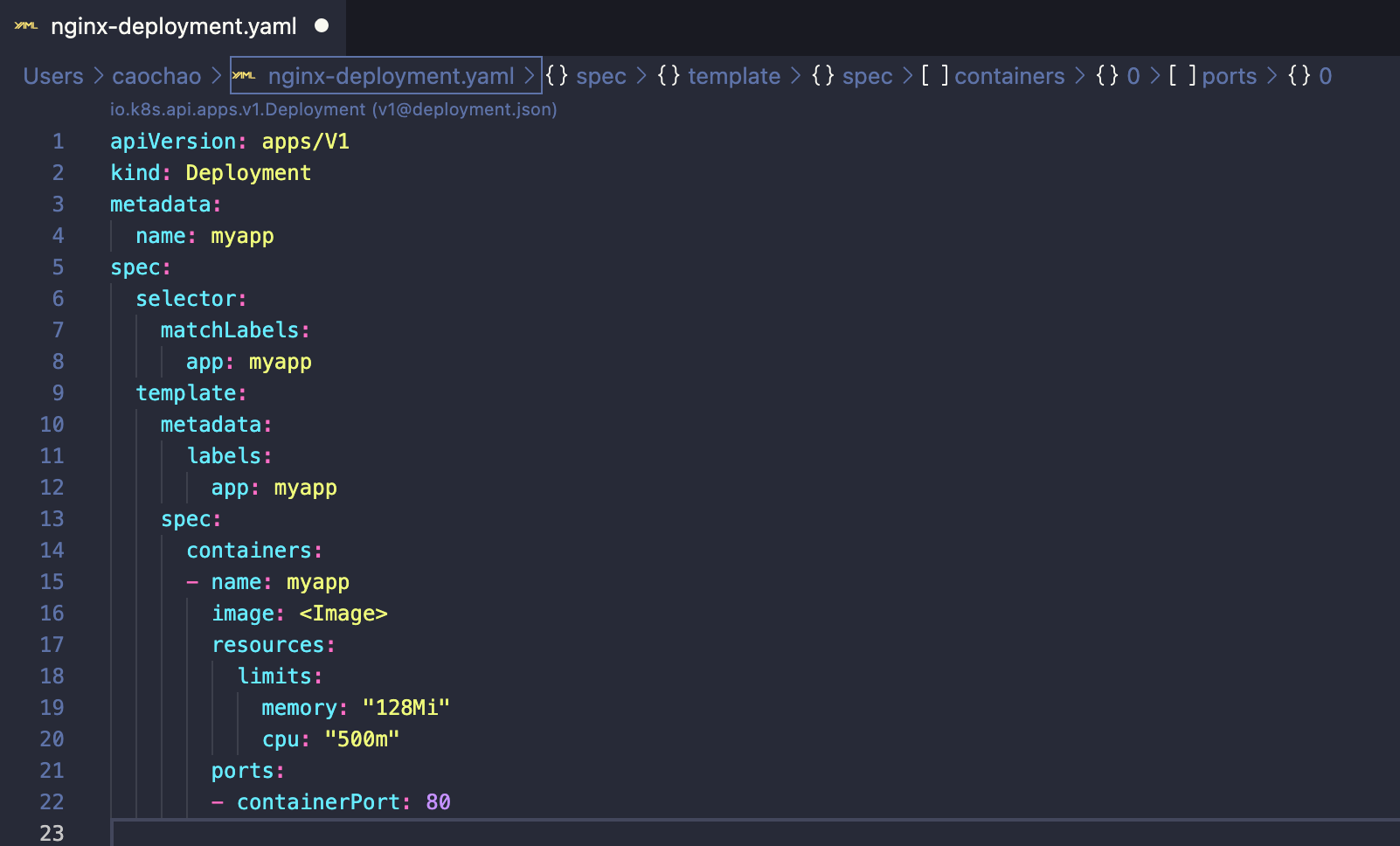
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1 |
apply the configuration file
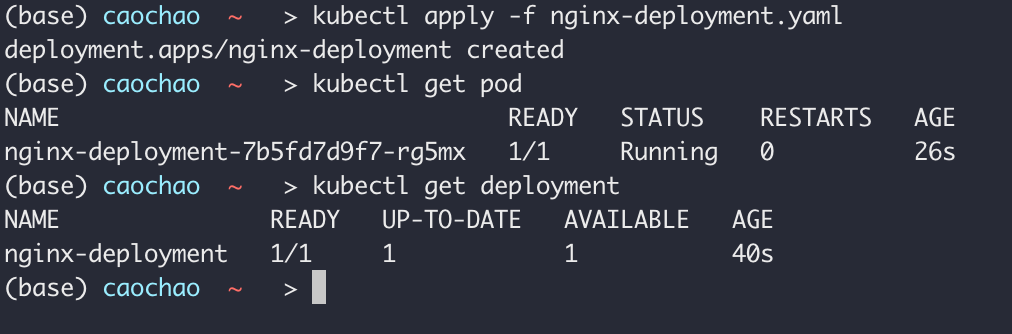
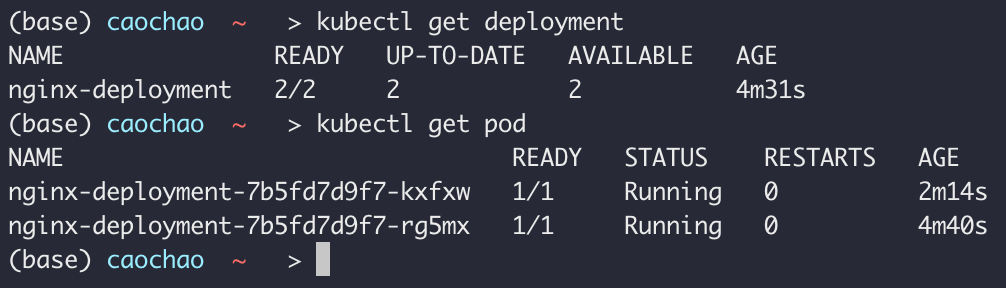
change the number of replicas
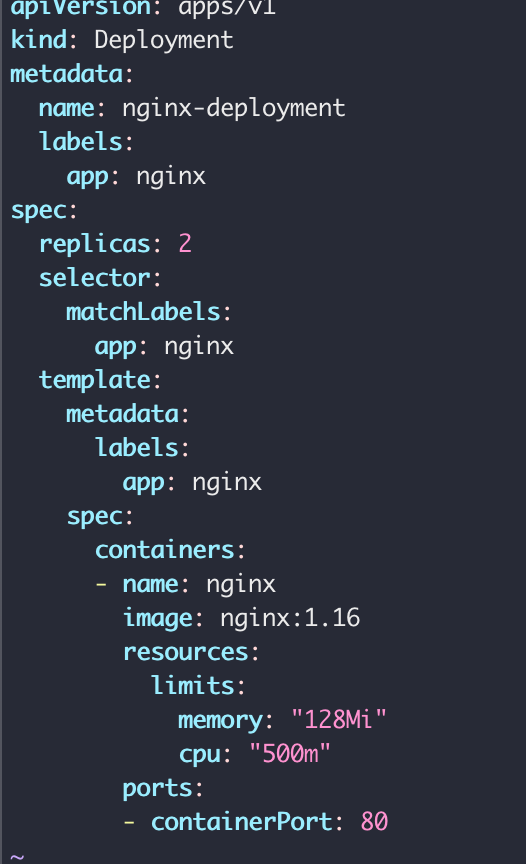
K8s knows when to create or update deployment
We can get
Summarize the kubectl commands
CRUD commands
| 功能 | 指令 |
|---|---|
| create deployment | Kubectl create deployment [name] |
| Edit deployment | Kubectl edit deployment [name] |
| Delete deployment | Kubectl delete deployment [name] |
Status of different k8s components
Kubectl get nodes | pod | services | relicaset | deployment
Debugging pods
| 功能 | 指令 |
|---|---|
| Log to console | kubectl logs [pod name] |
| Get Interactive Terminal | Kubectl exec -it [pod name] – bin/bash |
| Git info about pod | kubectl describe pod [pod name] |
Use configuration file for CRUD
| 功能 | 指令 |
|---|---|
| Apply a configuration file | kubectl apply -f [file name] |
| Delete with configuration file | kubectl delete -f [file name] |
K8s Yaml Configuration File
3 parts of a K8s configuration file
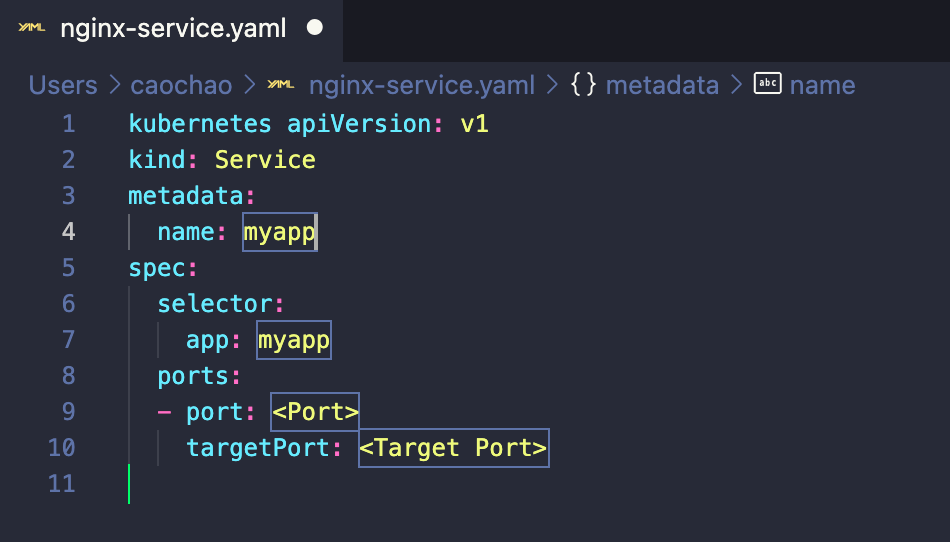
Service Template
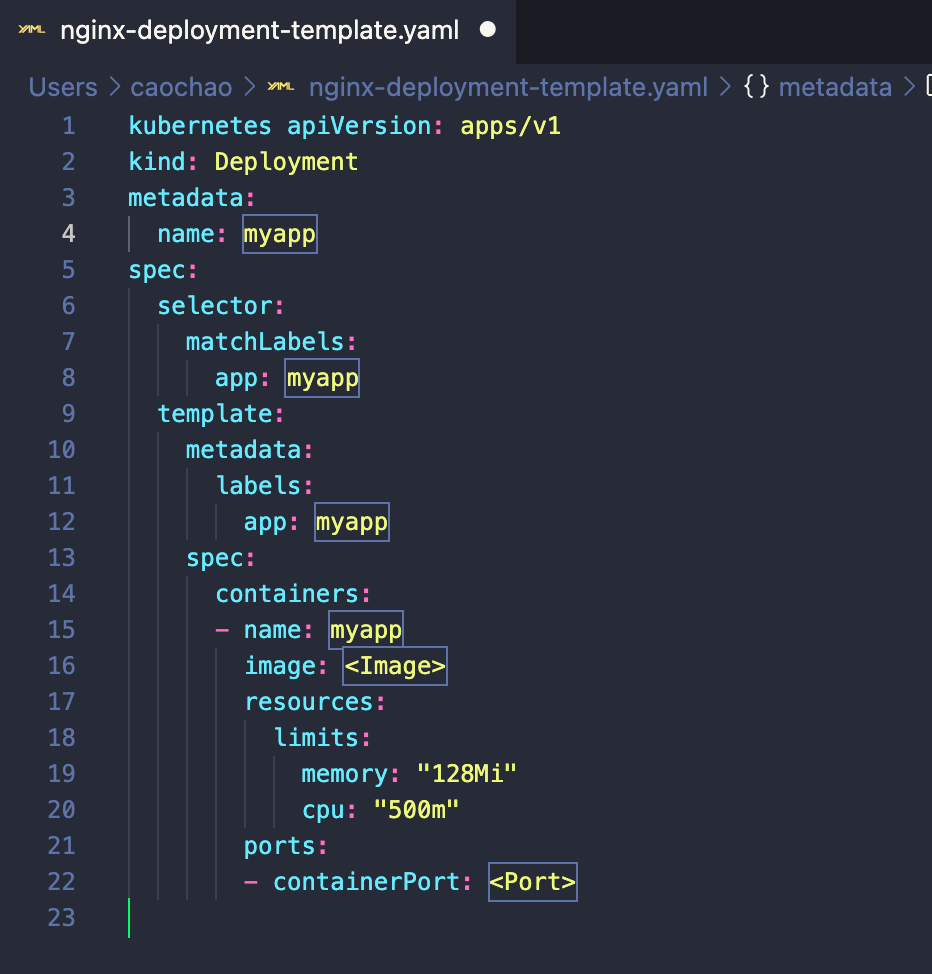
Deployment Template
Each configuration file 3 parts
kind declares what we want to create
metadata
Name
specification
details we want to deploy
Attributes of “spec“ are specfic to the kind
status
automatically generated and added by Kubernetes
Desired != Actual ?
K8s updates state continuously
Where does K8s get this status data?
etcd
Etcd holds the current status of any K8s component
Format of configuration file
YAML configuration file
智能,人性化,好修改;可以自主编辑然后能保存到云库再共享
Blueprint for pods (Template)
Deployment manage Pods
Template
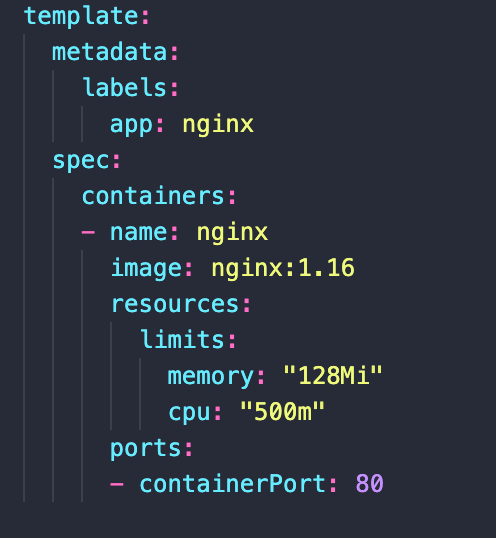
- Has it’s own “metadata” and “spec” section
- Applies to pod
- Blueprint for a pod
- Name?
- Ports?
- Image?
Connecting components
Labels & Selectors & Ports
Deployment metadata
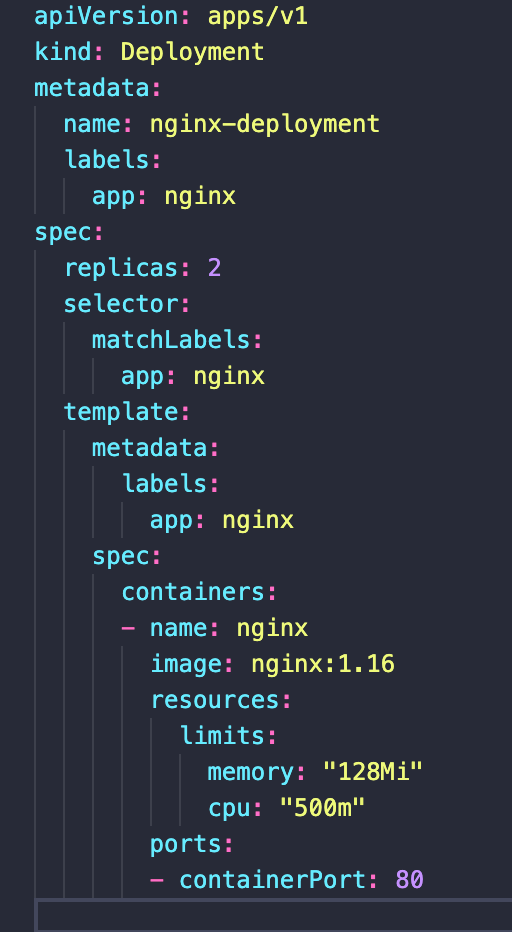
Service metadata
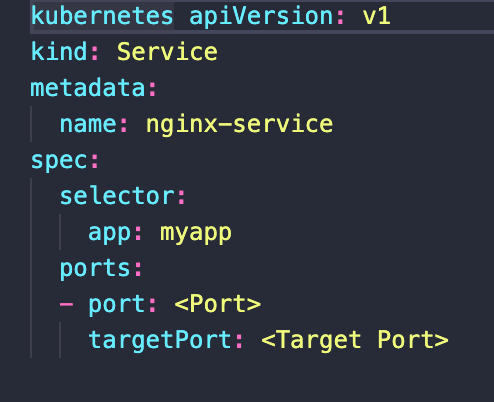
connecting Deployment to Pods
any key-value pair for component
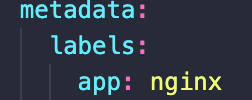
Pods get the label through the template blueprint
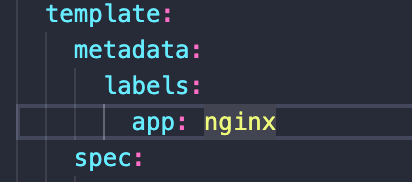
The label is matched by the selector in services

Selector in service match labels (2) in deployment
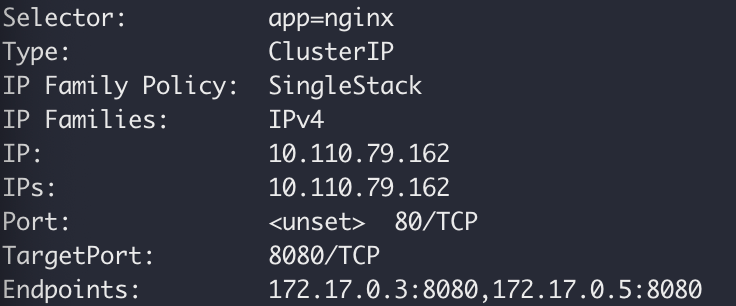
Ports in Service and Pod
DB service —> (port:80) ngnix Service —> (targetPort:8080) Pod
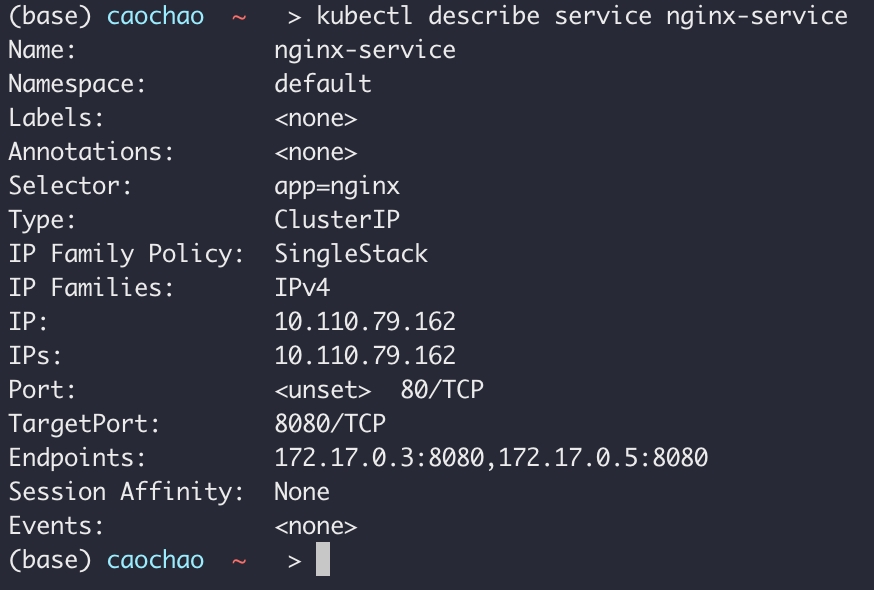
对应service中的部分:
more information
1 | kubectl get pod -o wide |

Status automatically generated?
1 | kubectl get deployment nginx-deployment -o yaml > nginx-deployment-result.yaml |
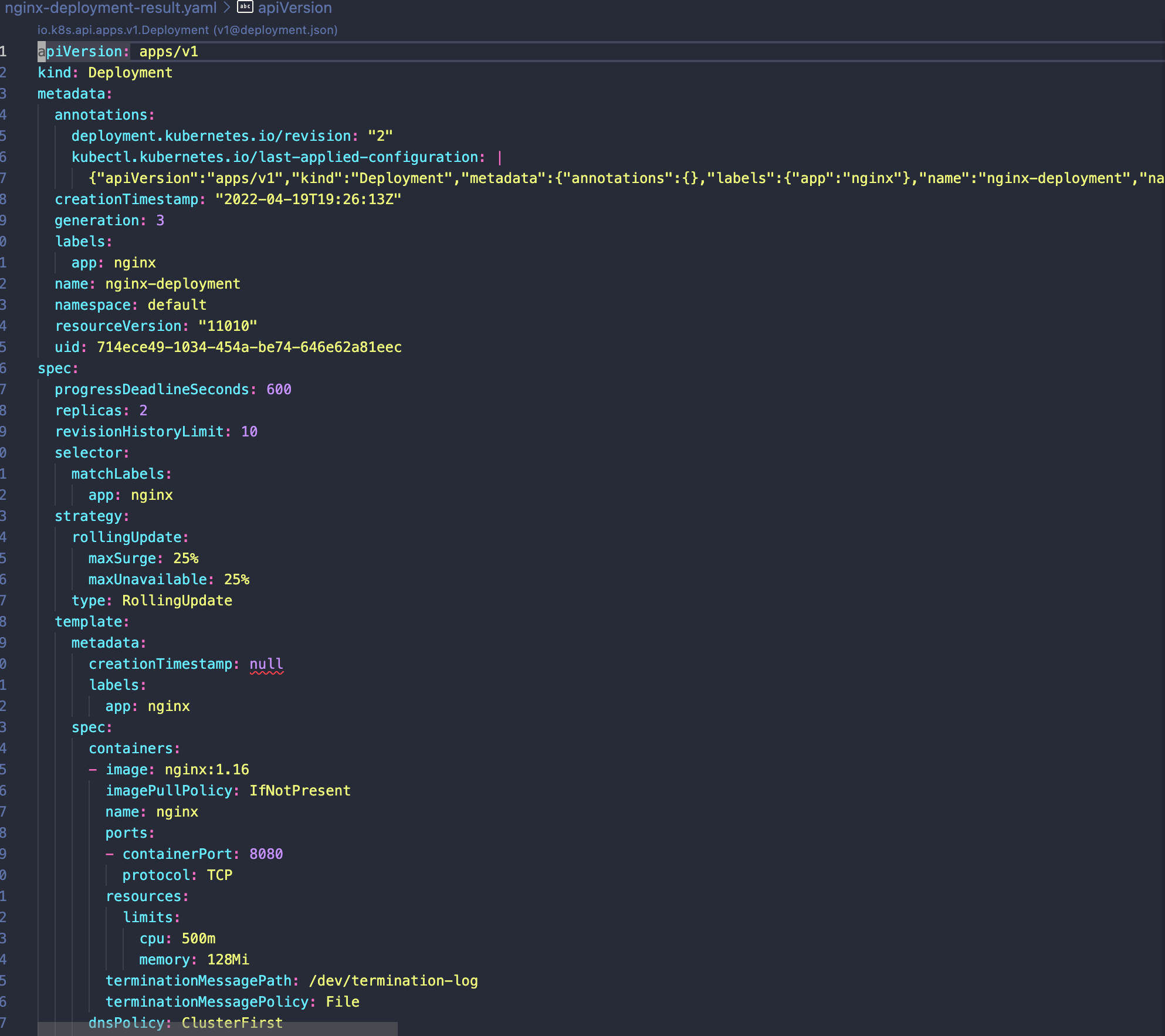
删除配置和服务
1 | kubectl delete -f nginx-deployment.yaml |
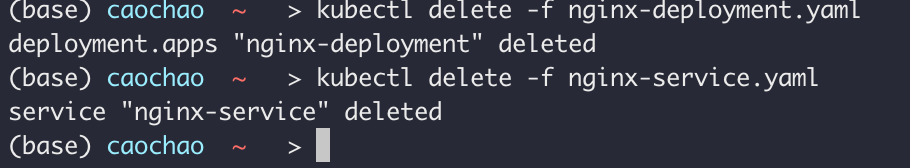
Hands-On Demo
Mongo-express + mongoDB
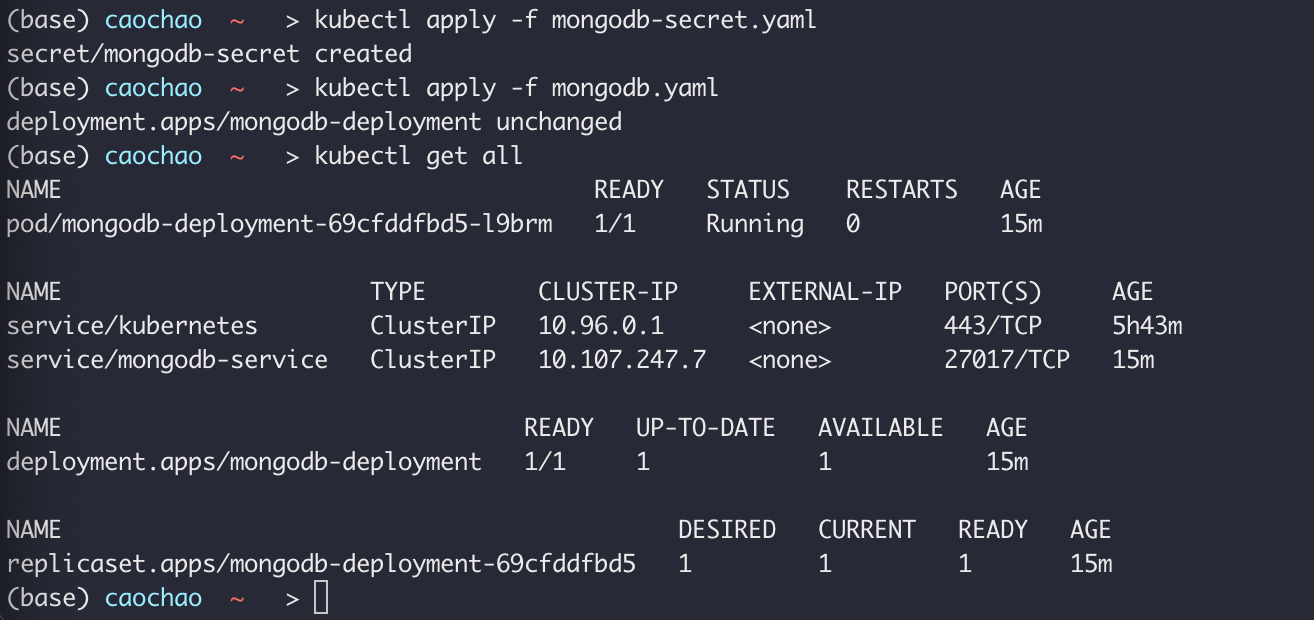
1 | Kubectl get all |
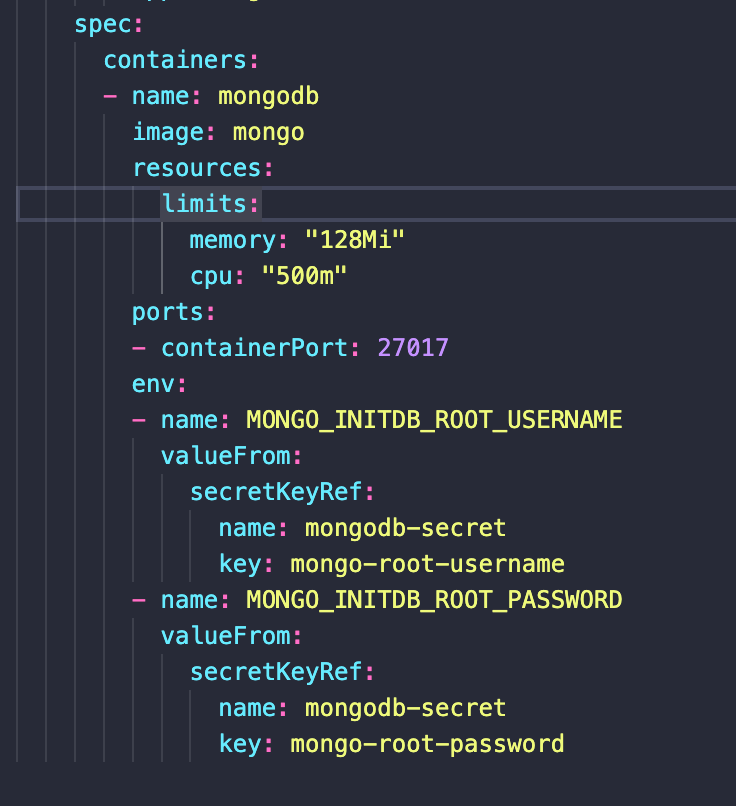
create mongodb file
Pod blueprint
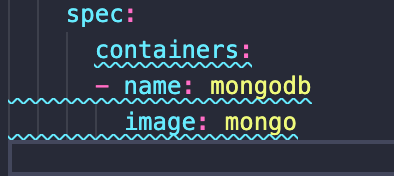
mongodb port: 27017
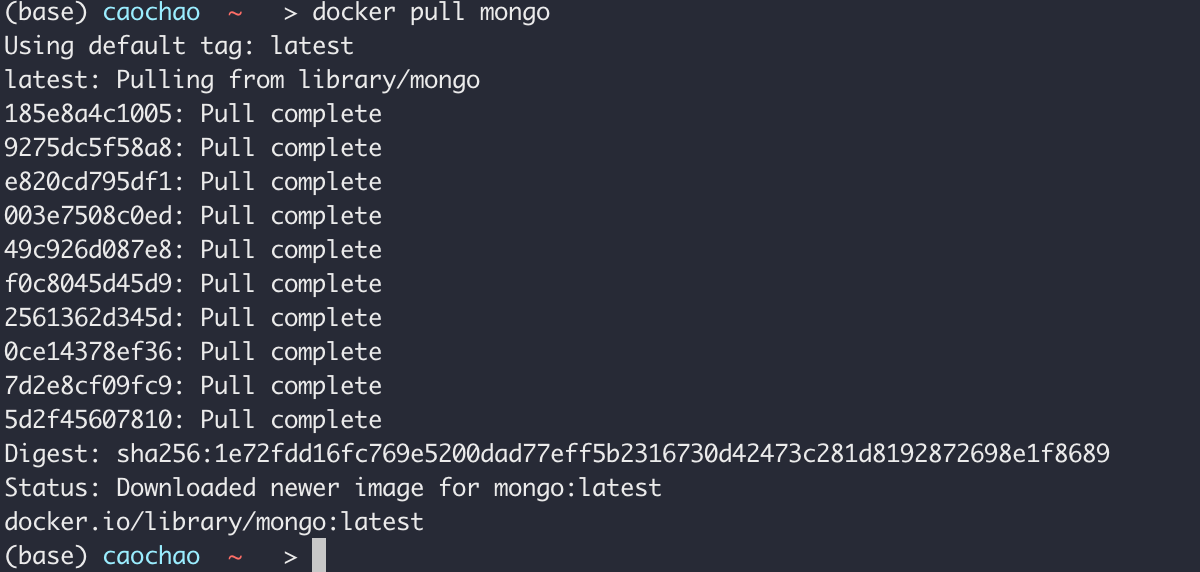
Deployment Config File is checked into repository
Username and password should not go here
Secret lives in k8s, not in the repository
Value: Username and password
Secret Configuration File
– kind: Secret
– metadata/name: a random name
– type: “Opaque” -default for arbitrary key - value pairs
– data: the actual contents - key-value pairs
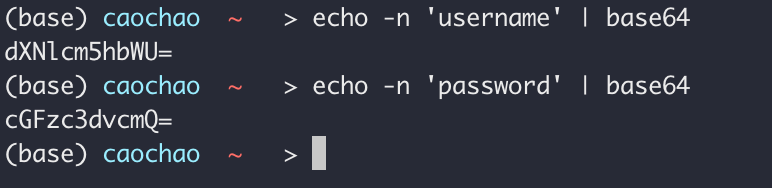
加密用户名和密码
1 | echo -n 'username' | base64 |
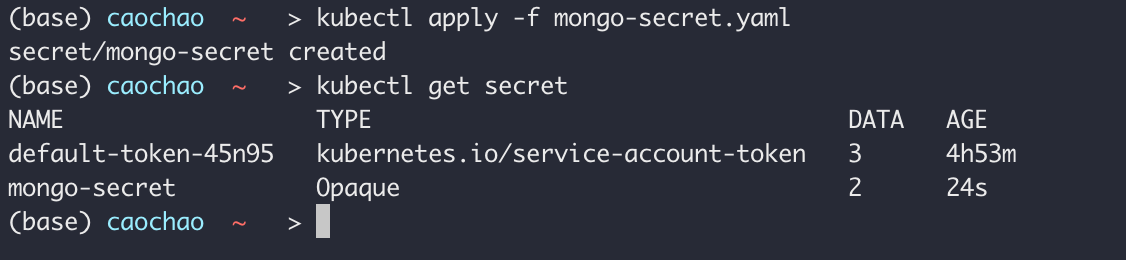
Secret must be created before the Deployment
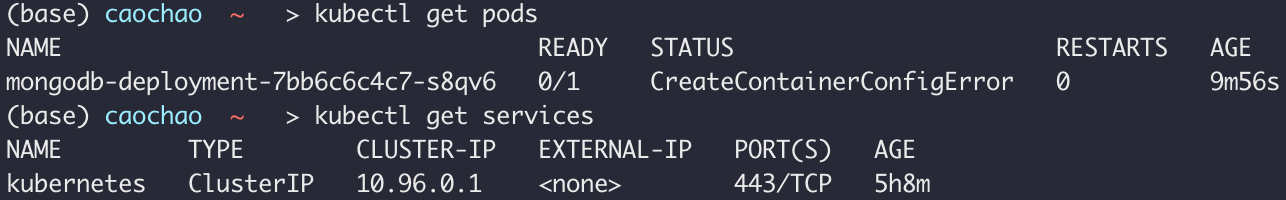
Secret can be referenced now in Deployment
需要限制资源
Error:
1 | kubectl get pods |
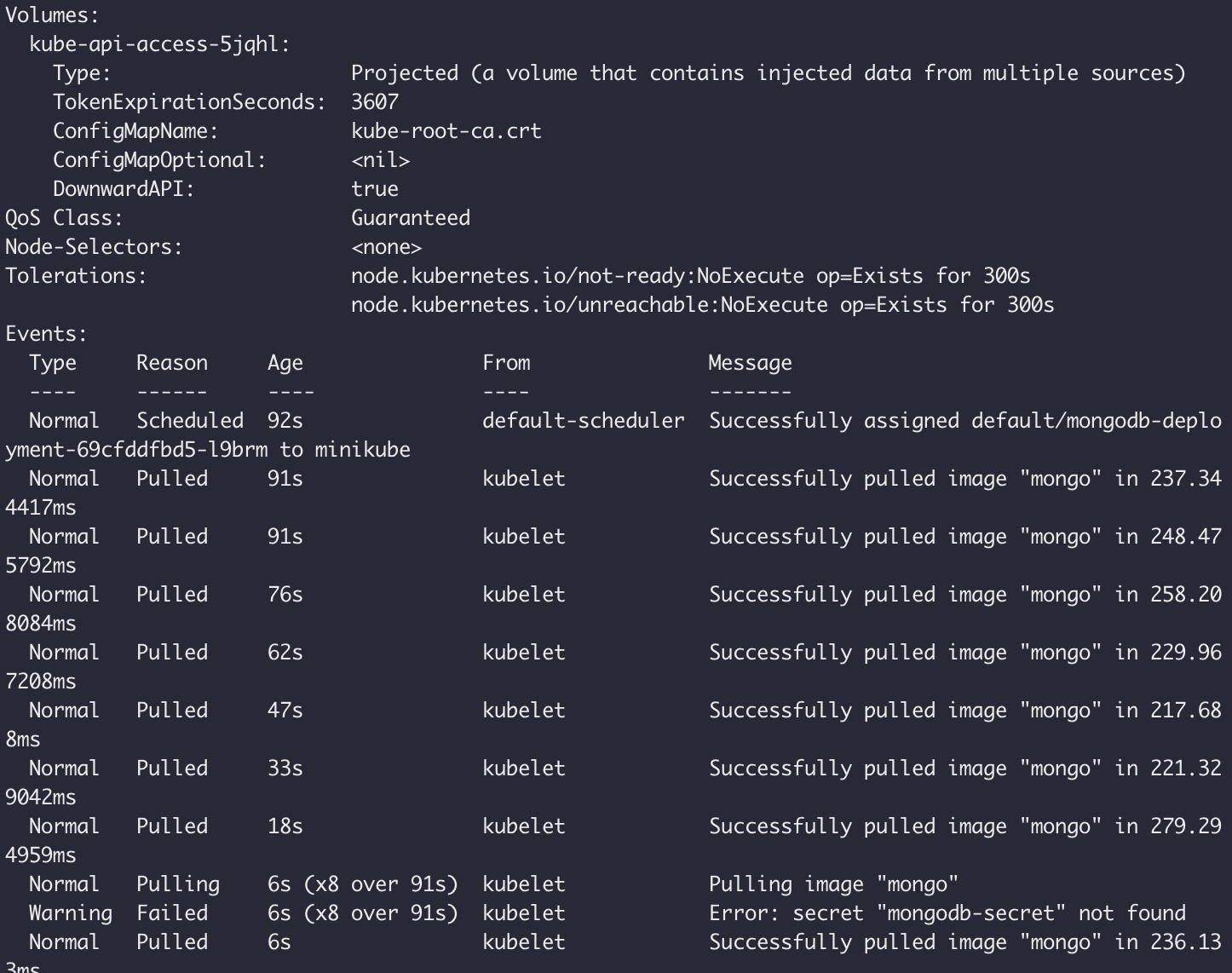
Possible Solution:

Solution:
create secrets before deployment!!!!!
创建ConfigMAp
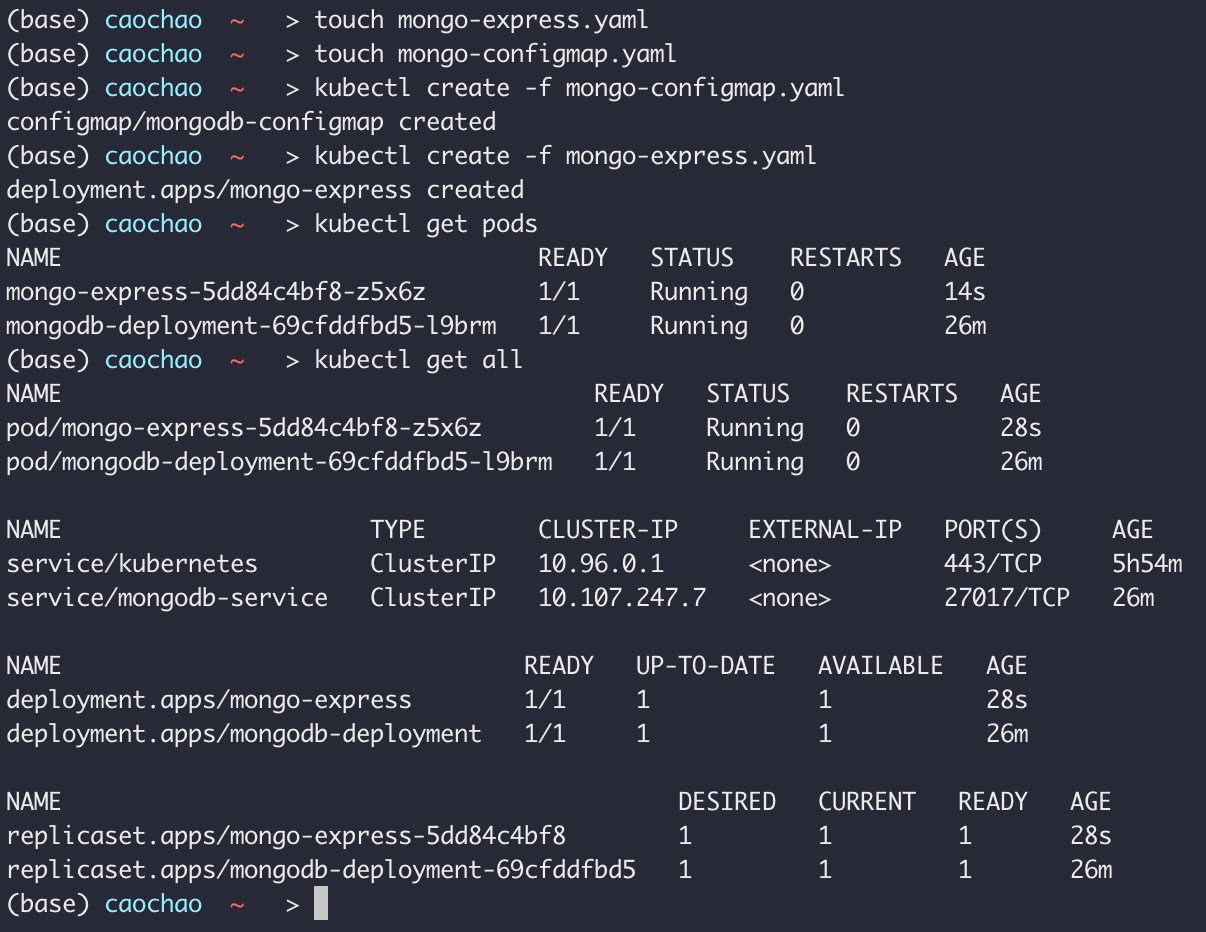
Database connected
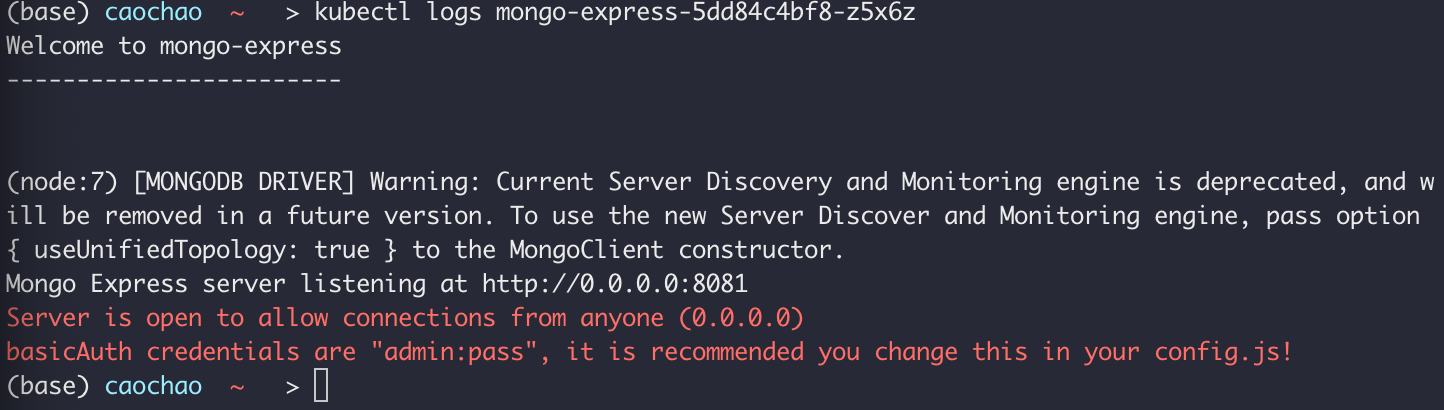
Create mongoexpress-service
How to make it an EXternal Service?
-type: “LoadBalancer”
BUT, internal service also acts as a loaderbalancer!
nodePort: for exteral IP address; set port you need to put into the browser
(30000-32767)
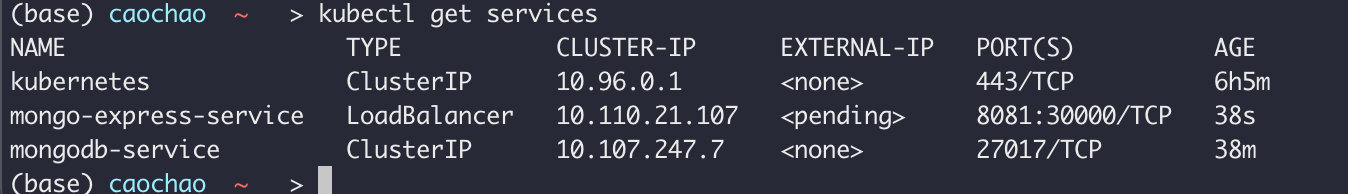
1 | minikube service mongo-express-service |